Mri or Ultrasound Which Best for Rectal Resection
MRI is arguably the most complete imaging modality for local staging of rectal cancer. Terminology of rectal cancer staging.

Comparison Of Three Dimensional Rectosonography Rectal Endoscopic Sonography And Magnetic Resonance Imaging Performances In The Diagnosis Of Rectosigmoid Endometriosis European Journal Of Obstetrics And Gynecology And Reproductive Biology
MRI is superior to CT for assessing invasion to adjacent organs.
. MRI helps to decide which method to use including shaving disc excision or segmental resection for the surgical treatment of rectal endometriosis. Chemoradiation therapy MRI rectal cancer recurrence staging DOI102214AJR. MRI is highly accurate for differentiating T1-T2 disease from T3 and T4 disease an important distinction as patients with.
An endorectal coil is a surface coil and provides very good images of the wall of the organ but offers limited information on surrounding structures. Endoscopic ultrasound is the imaging modality of choice for small and small superficial tumors. In some cases however a different modality may be preferable.
MRI PPV is higher for both muscularis and submucosalmucosal infiltration. MRI will help your healthcare provider decide which treatment is best for your health condition. International guidelines dictate that magnetic resonance imaging MRI should be part of the primary standard work up of patients with rectal cancer because MRI can accurately identify the main risk factors for local recurrence and.
High-resolution MRI of pelvis with distension of rectum by positive contrast agent is an investigation of choice for local staging of rectal cancer due to its superior soft tissue contrast resolution. MRI offers the advantages of its superior soft-tissue contrast multiplanar imaging and functional assessment. In mid rectum correlation coefficients were 092 p 001 for ERUS and 044 p 038 for MRI.
Twenty patients with rectal cancer who did not receive preoperative chemoradiotherapy and. Invasive surgeries LAR- low anterior resection APR- abdominoperineal resection. Ideally higher field strengths eg 15 T or 30 T are preferred with some studies dem- onstrating similar accuracies for.
However its accuracy depends on both user expertise as well as correct technique during the procedure. Rectal MR with a phased array coil typically cannot distinguish between T1 and T2 status as the layers of bowel wall are not resolved. Evaluated best by endoscopic rectal ultrasound which can directly visualize the layers of the bowel wall.
Some authors suggest that a circumferential resection margin CRM of less than 1 or 2 mm the exact cut-off is debated confers a poorer prognosis and patients should be considered for neoadjuvant treatment 6. Transrectal ultrasound TRUS is an accu-rate imaging modality for differentiating T1 from T2 tumors and is similar to MRI in dif-ferentiating T2 from T3 tumors 68. The women with rectal endometriosis should be assessed with MRI which has a value both for the preoperative diagnosis of rectal endometriosis and preoperative risk evaluation of performing.
Approach to rectal MRI. In recent years MRI has emerged as a leading modality for simultaneous evaluation of local and nodal staging of rectal cancers. Sphincteric resection or abdominoperineal resection APR surgeries are attempted 5.
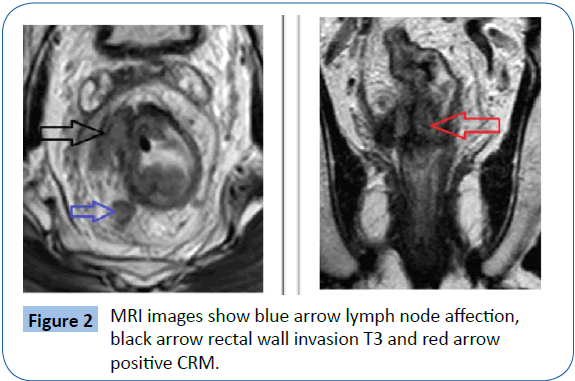
No preprocedural bowel cleansing regimen intravenous contrast material nor endorectal coil is necessary. MRI is definitely superior to CT in local staging except in T1 T2 stage where both have comparable accuracies 7 Figures 1 and 2. T3 invasion into the mesorectal fat T3-tumors grow through the muscularis propria into the surrounding mesorectum.
Up to 10 cash back RES offers several theoretical advantages over MRI. Sideration in the diagnosis and staging of rectal cancer by endoscopic ultrasound EUS and magnetic resonance imaging MRI. Compared to RES MRI is valuable in detecting rectal endometriosis but less accurate in detecting submucosalmucosal involvement.
Wide-bore and open-bore MRI machines provide some relief from the feeling of confinement and the use of sedatives can help some patients tolerate the procedure. A variety of examinations have been used for preop- erative staging of rectal cancer including digital rectal examination endorectal endoscopic ultrasound CT and MRI. However RES has a better NPV for the detection of submucosalmucosal infiltration.
While MRI is used routinely for preoperative rectal cancer imaging ERUS can provide additional assessment of CRM for mid or distal rectal lesions. In distal rectum correlation coefficients were 071 p 002 for ERUS and -010 p 079 for MRI. Each set lasts 14 seconds to several minutes.
Endorectal ultrasound is more accurate for this purpose. Most times an MRI scan of this area involves taking 8 or 9 sets of pictures. A rectal MRI takes pictures of your pelvic area lower abdomen.
To assess the correlation between endorectal ultrasound ERUS and magnetic resonance imaging MRI in predicting the circumferential resection margin CRM status of patients with mid-low rectal cancer without preoperative chemoradiotherapy. Multiplanar high-resolution 3-mm section thickness T2-weighted images are the primary sequences used for rectal cancer staging. Tumors that remain limited to the rectal wall are therefore typically grouped as cT1-2 on MRI.
High-field-strength MRI provides fast image ac- quisition high spatial resolution and high signal- to-noise ratio improving the visibility of the rectal wall 25. Correct field alignment through the long axis of the rectum is an important determinant of accuracy. The same organ can be easily seen in an MRI picture.
Computed tomography CT magnetic resonance imaging MRI and 18-fluorideoxyglucose positron emission tomography 18 FDG-PET are historically the most accurate imaging techniques for diagnosing liver metastases. Recently the combination of diffusion-weighted imaging and hepatospecific contrast media such as gadoxetic acid in MRI. Rectal cancer response assessment.
Real-time imaging high spatial resolution direct visualization of DIE lesion better assessment of DIE location from the anal margin evaluation of the circumference of digestive involvement and improved detection of multifocal lesions 11 12 13. MRI requires more expensive and much larger machinery than ultrasound. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI with both endorectal and pelvic phased array coils is the gold standard especially in oncological rectal examination.

Rectal Ultrasound Image A Cystic Lesion Between The Rectum And The Download Scientific Diagram

Comparative Study Between The Role Of Trans Rectal Ultrasound And Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Preoperative Staging Of Rectal Carcinoma
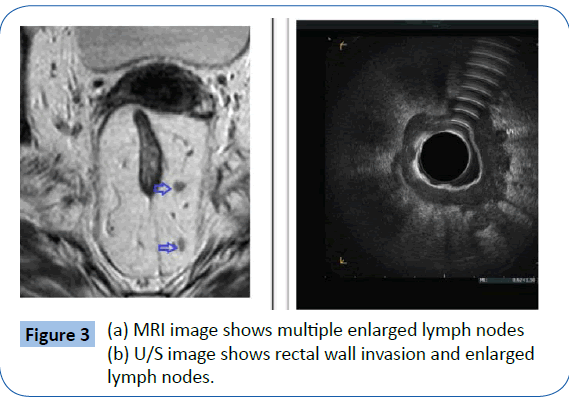
Comparative Study Between The Role Of Trans Rectal Ultrasound And Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Preoperative Staging Of Rectal Carcinoma
No comments for "Mri or Ultrasound Which Best for Rectal Resection"
Post a Comment